Plotly 热图
热图(或热图)是数据的图形表示,其中包含在矩阵中的各个值表示为颜色。热图的主要目的是更好地可视化数据集中的位置/事件量,并帮助将查看者引导至数据可视化中最重要的区域。
由于它们依赖颜色来传达值,因此热图可能最常用于显示更通用的数值视图。热图在吸引人们关注趋势方面非常通用和高效,正是由于这些原因,它们在分析社区中变得越来越流行。
热图天生就不言自明。阴影越深,数量越大(值越高,分散越紧密等)。 Plotly 的 graph_objects 模块包含 热图() 功能。它需要 x, y and z 属性。它们的值可以是列表、numpy 数组或 Pandas 数据框。
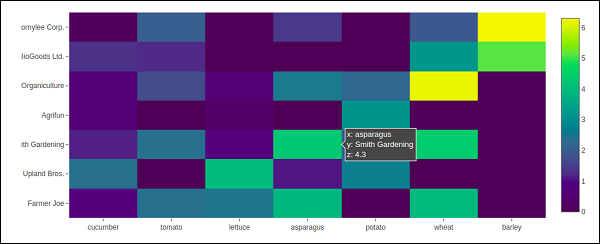
在下面的示例中,我们有一个二维列表或数组,它将数据(不同农民的收获吨/年)定义为颜色代码。然后我们还需要两张农民名单和他们种植的蔬菜。
vegetables = [ "cucumber", "tomato", "lettuce", "asparagus", "potato", "wheat", "barley" ] farmers = [ "Farmer Joe", "Upland Bros.", "Smith Gardening", "Agrifun", "Organiculture", "BioGoods Ltd.", "Cornylee Corp." ] harvest = np.array( [ [0.8, 2.4, 2.5, 3.9, 0.0, 4.0, 0.0], [2.4, 0.0, 4.0, 1.0, 2.7, 0.0, 0.0], [1.1, 2.4, 0.8, 4.3, 1.9, 4.4, 0.0], [0.6, 0.0, 0.3, 0.0, 3.1, 0.0, 0.0], [0.7, 1.7, 0.6, 2.6, 2.2, 6.2, 0.0], [1.3, 1.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 3.2, 5.1], [0.1, 2.0, 0.0, 1.4, 0.0, 1.9, 6.3] ] ) trace = go.Heatmap( x = vegetables, y = farmers, z = harvest, type = 'heatmap', colorscale = 'Viridis' ) data = [trace] fig = go.Figure(data = data) iplot(fig)
上述代码的输出如下: