SciPy Ndimage
SciPy ndimage 子模块专用于图像处理。这里,ndimage是指n维图像。
图像处理中一些最常见的任务如下:
- 输入/输出,显示图像
- 基本操作:裁剪、翻转、旋转等。
- 图像过滤:去噪、锐化等
- 图像分割:标注不同物体对应的像素
- 分类
- 特征提取
- 登记
让我们讨论如何使用 SciPy 实现其中的一些。
打开和写入图像文件
The 杂项包 在 SciPy 中带有一些图像。我们使用这些图像来学习图像操作。让我们考虑下面的例子。
from scipy import misc
f = misc.face()
misc.imsave('face.png', f) # uses the Image module (PIL)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(f)
plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。

任何原始格式的图像都是由矩阵格式中的数字表示的颜色组合。机器仅根据这些数字来理解和操作图像。 RGB 是一种流行的表示方式。
让我们看看上图的统计信息。
from scipy import misc face = misc.face(gray = False) print face.mean(), face.max(), face.min()
上述程序将生成以下输出。
110.16274388631184, 255, 0
现在,我们知道图像是由数字组成的,因此数字值的任何变化都会改变原始图像。让我们对图像进行一些几何变换。基本的几何操作是裁剪
from scipy import misc face = misc.face(gray = True) lx, ly = face.shape # Cropping crop_face = face[lx / 4: - lx / 4, ly / 4: - ly / 4] import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(crop_face) plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。
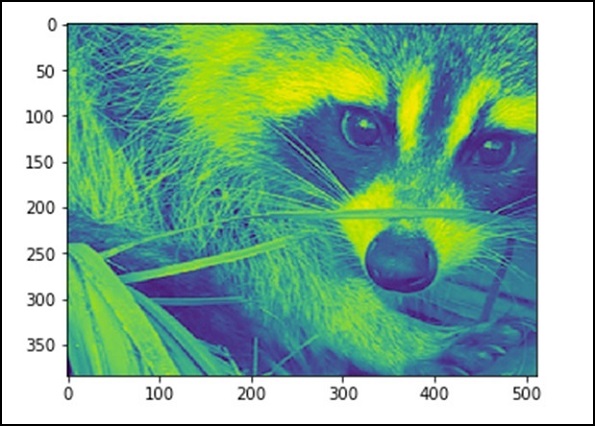
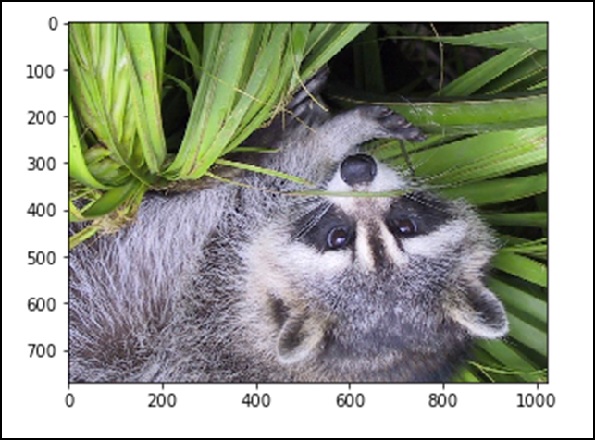
我们还可以执行一些基本操作,例如将图像上下颠倒,如下所述。
# up <-> down flip from scipy import misc face = misc.face() flip_ud_face = np.flipud(face) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(flip_ud_face) plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。

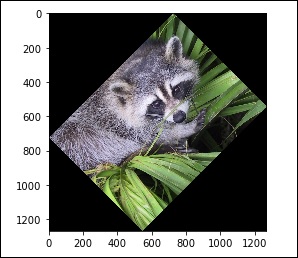
除此之外,我们还有 旋转()函数 ,它以指定的角度旋转图像。
# rotation from scipy import misc,ndimage face = misc.face() rotate_face = ndimage.rotate(face, 45) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(rotate_face) plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。
Filters
让我们讨论一下过滤器如何帮助图像处理。
什么是图像处理中的过滤?
过滤是一种用于修改或增强图像的技术。例如,你可以过滤图像以强调某些特征或删除其他特征。使用过滤实现的图像处理操作包括平滑、锐化和边缘增强。
滤波是一种邻域运算,其中输出图像中任何给定像素的值是通过对相应输入像素的邻域中的像素值应用某种算法来确定的。现在让我们使用 SciPy ndimage 执行一些操作。
Blurring
模糊被广泛用于减少图像中的噪声。我们可以执行一个过滤操作,看看图像的变化。让我们考虑下面的例子。
from scipy import misc face = misc.face() blurred_face = ndimage.gaussian_filter(face, sigma=3) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(blurred_face) plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。
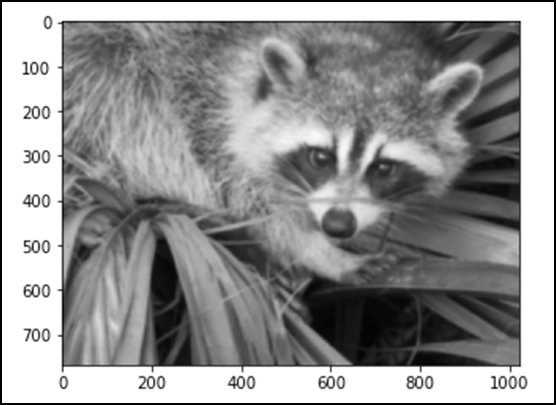

sigma 值表示五级的模糊程度。我们可以通过调整 sigma 值看到图像质量的变化。有关模糊的更多详细信息,请单击 → DIP(数字图像处理)教程。
边缘检测
让我们讨论边缘检测如何帮助图像处理。
什么是边缘检测?
边缘检测是一种图像处理技术,用于在图像中找到对象的边界。它通过检测亮度的不连续性来工作。边缘检测用于图像处理、计算机视觉和机器视觉等领域的图像分割和数据提取。
最常用的边缘检测算法包括
- Sobel
- Canny
- Prewitt
- Roberts
- 模糊逻辑方法
让我们考虑下面的例子。
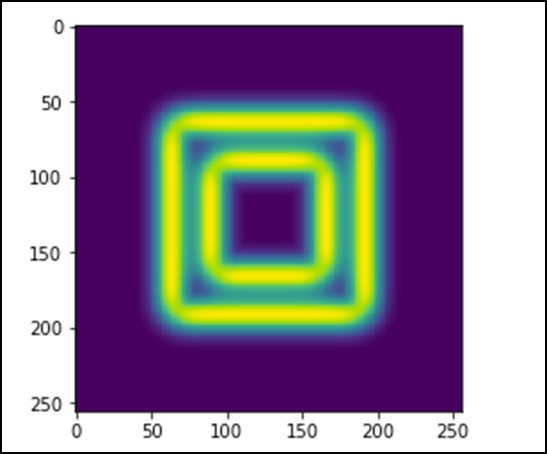
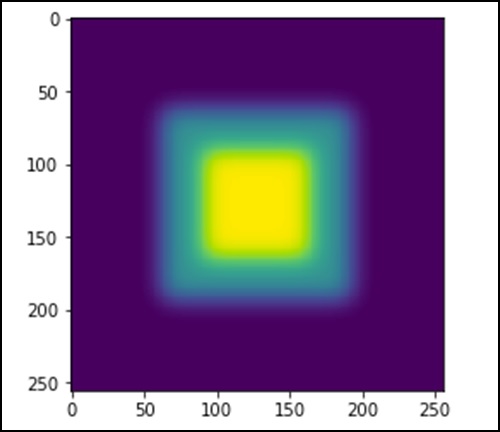
import scipy.ndimage as nd import numpy as np im = np.zeros((256, 256)) im[64:-64, 64:-64] = 1 im[90:-90,90:-90] = 2 im = ndimage.gaussian_filter(im, 8) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(im) plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。
图像看起来像一个正方形的颜色块。现在,我们将检测这些彩色块的边缘。在这里,ndimage 提供了一个名为 Sobel 来执行这个操作。鉴于,NumPy 提供 Hypot 函数将两个结果矩阵合并为一个。
让我们考虑下面的例子。
import scipy.ndimage as nd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt im = np.zeros((256, 256)) im[64:-64, 64:-64] = 1 im[90:-90,90:-90] = 2 im = ndimage.gaussian_filter(im, 8) sx = ndimage.sobel(im, axis = 0, mode = 'constant') sy = ndimage.sobel(im, axis = 1, mode = 'constant') sob = np.hypot(sx, sy) plt.imshow(sob) plt.show()
上述程序将生成以下输出。