R时间序列分析
时间序列是一系列数据点,其中每个数据点都与时间戳相关联。一个简单的例子是股票市场上某一天不同时间点的股票价格。另一个例子是一个地区一年中不同月份的降雨量。 R 语言使用许多函数来创建、操作和绘制时间序列数据。时间序列的数据存储在一个名为的 R 对象中 时间序列对象 .它也是一个 R 数据对象,如矢量或数据框。
时间序列对象是通过使用 ts() 功能。
语法
的基本语法 ts() 时间序列分析中的函数是:
timeseries.object.name <- ts(data, start, end, frequency)
以下是使用的参数说明:
-
data 是包含时间序列中使用的值的向量或矩阵。
-
start 指定时间序列中第一次观察的开始时间。
-
end 指定时间序列中最后一次观察的结束时间。
-
频率 指定每单位时间的观察次数。
除了参数“数据”之外,所有其他参数都是可选的。
例子
考虑从 2012 年 1 月开始的某个地方的年降雨量详细信息。我们创建一个为期 12 个月的 R 时间序列对象并绘制它。
# Get the data points in form of a R vector. rainfall <- c(799,1174.8,865.1,1334.6,635.4,918.5,685.5,998.6,784.2,985,882.8,1071) # Convert it to a time series object. rainfall.timeseries <- ts(rainfall,start = c(2012,1),frequency = 12) # Print the timeseries data. print(rainfall.timeseries) # Give the chart file a name. png(file = "rainfall.png") # Plot a graph of the time series. plot(rainfall.timeseries) # Save the file. dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码时,会产生如下结果和图表:
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep 2012 799.0 1174.8 865.1 1334.6 635.4 918.5 685.5 998.6 784.2 Oct Nov Dec 2012 985.0 882.8 1071.0
时间序列图:
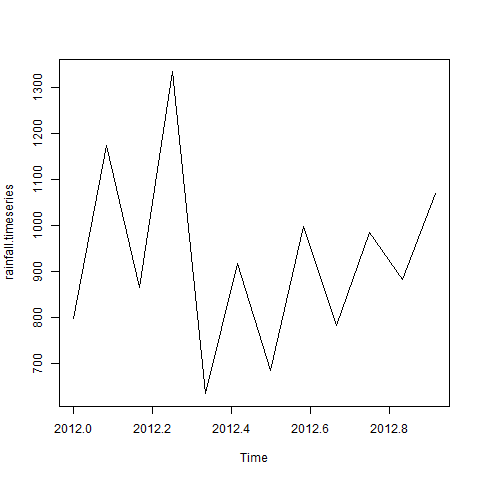
不同的时间间隔
的价值 频率 ts() 函数中的参数决定了测量数据点的时间间隔。值 12 表示时间序列为 12 个月。其他值及其含义如下:
-
频率 = 12 钉住一年中每个月的数据点。
-
频率 = 4 钉住一年中每个季度的数据点。
-
频率 = 6 每隔 10 分钟固定一个小时的数据点。
-
频率 = 24*6 每天每 10 分钟固定一次数据点。
多个时间序列
我们可以通过将两个系列组合成一个矩阵,在一个图表中绘制多个时间序列。
# Get the data points in form of a R vector. rainfall1 <- c(799,1174.8,865.1,1334.6,635.4,918.5,685.5,998.6,784.2,985,882.8,1071) rainfall2 <- c(655,1306.9,1323.4,1172.2,562.2,824,822.4,1265.5,799.6,1105.6,1106.7,1337.8) # Convert them to a matrix. combined.rainfall <- matrix(c(rainfall1,rainfall2),nrow = 12) # Convert it to a time series object. rainfall.timeseries <- ts(combined.rainfall,start = c(2012,1),frequency = 12) # Print the timeseries data. print(rainfall.timeseries) # Give the chart file a name. png(file = "rainfall_combined.png") # Plot a graph of the time series. plot(rainfall.timeseries, main = "Multiple Time Series") # Save the file. dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码时,会产生如下结果和图表:
Series 1 Series 2 Jan 2012 799.0 655.0 Feb 2012 1174.8 1306.9 Mar 2012 865.1 1323.4 Apr 2012 1334.6 1172.2 May 2012 635.4 562.2 Jun 2012 918.5 824.0 Jul 2012 685.5 822.4 Aug 2012 998.6 1265.5 Sep 2012 784.2 799.6 Oct 2012 985.0 1105.6 Nov 2012 882.8 1106.7 Dec 2012 1071.0 1337.8
多重时间序列图:

